SPE TES
Espace membre
TS Sujets
BAC S JUIN 2010
- Bac 2010. S. Ex 1 partie A
- INFOEX1 Partie B BAC S JUIN 10
- EX2 BAC S GRAPHIQUE 22 juin 10
- INFO EX2 1 ROC BAC S JUIN 10
- INFO EX2 2.a. BAC S juin 10
- INFO EX2 2b. BAC S JUIN10
- INFO EX2 2.c. BAC S juin 10
- INFO QUESTION3 EX2 S JUIN 10
- INFO QCM EX 3 BAC S JUIN 2010
- INFO EX4 BAC S JUIN 2010
- INFO EX4 FIG BAC S 22 JUIN 10
- INFO Ex 4 spé Bac S Juin 2010
- INFO EX 4 SPE BAC S JUIN 2010
- TEXTE EXERCICES BAC S 2010
Pages
- TEST 2 COMPLEXES
- INFO LISTE 3 EX ALGO
- SUR ORDI . GEOM. ESPACE 1S
- ACT.VECT. ESPACE 1 S 27MAI 09
- ACT;GEOM. ESP. LUNDI 25 MAI 1S
- GEOM. ESPACE 1S MAI 09
- AIDE 2 STAGE BTS 1
- AIDE STAGE BTS1
- Statistiques
- STAGE BTS1 SEPT . 09
- INFO TRAVAIL3 ORDI .GEO. ESP
- INFO DS n° 11 1S 3 juin 09
- INFO ACT GEOM ESP 25 MAI 09 1S
- INFO TRAVAIL 1 ORDI. GEOM ESP
- I ST. BTS
- DS n° 11 1S 3 juin 2009
- INFO EX 1 Feuille d'ex sur les
- 1.COURS SUITES TS sept 2012
- INFO DS n° 2 TS 27 oct. 2012
- INFO EX2 DV n°5 TS1 27 novemb
- INFO TEST ALGO EX1 27 nov 2012
- INFO TEST ALGO EX5 27 nov 201
- INFO TEST EX Ln Exp TS1 26
- Leçon ...n°7 Calcul intégral
- PYTHON 2.7 TEST BTS1 11/
- Cours : Proba.conditionnelles
- TS INFO EX4 BAC BLANC TS 15/2/
- INFO EX4 BAC BLANC 12 fév 2015
- t
- t
- INFO DEVOIR 22 mars 2016
- INFO EX 4 S 2016
- INFO EX2 DV TS spé maths
- INFO DV n° 5 TS spé 24 janv
- TEST TS spé math du 21 mars 2
- Petit Th. de Fermat TS spé ma
- SUJET BAC S Juin 2019
- Nombre de combinaisons à l'aid
Leçon 1 1S1
- ACTIVITE PREPARATOIRE
- Aide:Activ. prépar.Leçon1 1S
- INFO LISTE 2 EX ( Suite 2)
- INFO 2 TEST1 1S 1 ES OCT 10
- Aide Dv n° 1 1S sept 09
- INFO DV n° 1 Sept. 09 1S
- INFO 2 DV n° 1 Leçon 1 1S1
- INFO 3 DV n° 1 Sept. 09 1S
- DS n°1 1S1 7 / 10 / 09
- INFO 1 DS n° 1 1S1 07/10/09
- INFO 2 DS n° 1 1S1 7/10/09
- INFO3 DS n°1 1S1 07/10/09
- QUESTION LIBRE 1 1S1
- NOTES DS n ° 1 07 / 10 / 09
- INFO Activ .prépar 1S sept 09
- TEST 1 S et 1 ES Oct 2010
- INFO TEST 1 1S et 1ES
- INFO LISTE 2 EX ( Suite)
- INFO LISTE 2 d'EX Leçon 1
- LISTE 2 EX Leçon 1
- INFO LISTE II D'EX Leçon 1
- LISTE II D'EX Leçon 1
- QCM
- QCM
- QCM
- QCM :Fonctions- Enchaînements
- INFO LISTE D'EX
- SERIE 1 LISTE EX
- Leçon 1 ( Suite) 1S
- Fonctions ( Suite de la leçon)
- Fonctions 1S1
- INFO Activ .prépar 1S sept 09
Leçon 2 1S1
- LISTE A EX BARYCENTRE 1S
- INFO LISTE A EX BARY. 1S1
- DS n° 2 1S1 21 / 10 / 09
- INFO1 DS n°2 21/ 10/ 09 1S1
- INFO 2 DS n°2 21/10/09 1S1
- INFO 3 DS n° 2 21/10/09 1S1
- PARTIE FACUL. DS n° 2 21/10/09
- TRANSFORMATIONS ET BARYCENTRES
- INFO Complé. DS n°2 21/10/09
- NOTES DS n° 2 21/10/09 1S1
- QCM BARYCENTRE
- DV n° 2 1S1 24/10/09
- AIDE POUR LE DV n° 2 1S1
- INFO 1 DV n° 2 1S1 24/10/09
- INFO 2 DV n°2 1S1 24/ 10/09
- INFO 3 DV n°2 1S1 24/10/09
Leçon 3 1S1
- DV n°3 1S1 28 / 11/ 09
- AIDE 1 DV n° 3 1S1 nov.09
- INFO1 EX 74 ANGLE ORIEN.TRIGO
- INFO2 EX 74 ANGLE ORIEN. TRIGO
- EXERCICE 74 ANGLES ORIEN.TRIGO
- INFO EX 72 ANGLES ORIEN.TRIGO
- EXERCICE 72 ANGLES ORIEN TRIGO
- INFO EX 71 ANGLES ORIEN.
- EXERCICE 71 ANGLES ORIENTES
- INFO 4 DV n° 3 1S1 28 no. 09
- INFO 5 DV n° 3 1S 28 nov 09
- NOTES DS n ° 3 18 / 11 / 09
- INFO 3 DV n° 3 1S1 28 nov 09
- INFO 2 DV n° 3 1S1 28nov 09
- INFO 1 DV n°3 1S1 28 nov 09
- INFO 4 DS n° 3 1S1 18/11/09
- INFO EX 3 DS 3 1S1 18 nov 09
- INFO EX2 DS n° 3 1S 18 nov 09
- INFO 1 DS n° 3 1S1 18/11/09
- DS n 3 1S1 18 /11 / 09
- INFO5 FEUILLE EX ANGLES ORIEN.
- INFO 4 FEUILLE EX ANGLES ORIEN
- INFO3 FEUILLE EX ANGLES ORI.
- INFO2 Feuille EX ANGLE ORIEN.
- INFO1FEUILLE EX ANGLES ORIEN
- FEUILLE D' EX ANGLES ORIENTES
- AIDE 2 DV n° 3 1S1 09
Leçon4 1S1
- COORDONNEES POLAIRES
- LISTE D' EX. ANGLES ORIENTES
- NOTES DS n ° 4 19 / 12 / 09
- MODULO
- INFO LISTE EX ANGLE ORIEN TRIG
- Liste d'ex: Angle Orien. Trigo
- CHARIOT SUR UNE PENTE
- INFO QCM ANGLES ORIENTES TRIGO
- QCM ANGLE ORIENTE TRIGO. 1S1
- INFO EX ANGLE ORIEN 1S Déc.
- EXERCICE ANGLE ORIEN. Déc.09
- INFO DS n° 4 1S1
- DS n° 4 1S1 19 déc. 09
- FORMULES TRIGO. 1S1 DEC. 09
- INFO 2 LISTE EX TRIGO 1S1 DEC
- INFO 1LISTE:EX TRIG 1S1 Déc 09
- LISTE EX TRIGO 1S1 DEC . 09
- AIDE2 DV n° 4 1S1 janv.10
- AIDE DV n° 4 EX1 1S1 janv.10
- DV n°4 1S1 06 / 01/ 10
- INFO I LIST EX ANGLE ORIEN
- INFO 2 LISTE EX ANGLE ORIENTE
Leçon 5 1S1
- QCM TRIGO ET PROD SCAL
- QCM PRODUIT SCALAIRE
- INFO EX 4 DS 5 1S 27 JANV 10
- NOTES DS n ° 5 27 / 01 / 10
- INFO EX3 DS n° 5 1S 27/01/10
- INFO EX2 DS n° 5 1S 27/01/10
- INFO EX1DS 5 1S1 27/1/10
- INFO Question 1 EX2 DV5 Janv
- INFO Question 2 et 3 EX2 DV5
- INFO EX1 DVn°5 1S 23 JAN 10
- RESULTANTE EN PHY. Janv.10
- AIDE4 DV n° 5 1S1 janv.10
- AIDE3 DV n° 5 1S1 janv.10
- AIDE 2 DV n° 5 1S1 janv.10
- AIDE1 DV n° 5 1S1 janv.10
- DV n° 5 1S1 23/01/010
- INFO2 DV 4 6 janv 10 1S
- INFO1 DV n° 4 6 janv. 10 1S
- OLYMPIADES DE MATHS. SUJETS
- INFO 3 SERIE EX PROD SCAL
- INFO2 SERIE EX PROD SCAL
- INFO 1 SERI E EX PROD SCAL
- SERIE EX PROD SCAL 1S JANV10
Leçon 6 1S1
- AIDE DV n° 6 1S 17 /02/10
- Syst. lin. à deux inconnues
- INFO 3 DV n° 6 1S 17 fév 2010
- INFO 2 DV n° 6 1S 17 fév 2010
- INFO DV n° 6 1S1 17 fév 09
- Notes premier trimestre 1S
- Notes second trim. 1S
- NOTES DS n ° 6 17 / 02 / 10
- QCM SUR LA DERIVATION
- QCM DERIVATION 1S
- INFO EX DERIV. 1S mars 10
- EXERCICES DERIV 1S MARS 10
- EX Dériv. 1S mars 2010
- FEUILLE D' EX 20 fév. 2010
- FEUILLE D' EX 20 fév. 2010
- INFO 3 DS n° 6 1S1 17/02/10
- INFO 2 DS n° 6 1S1 17/02/10
- INFO 1 DS n° 6 1S1 17/02/10
- DS n° 6 1S1 17 février 2010
- INFO 2 FEUILLE EX 1S 12/ 2/10
- INFO FEUILLE EX 1S 12/02/10
- DV 6 1S 17/02/10
Leçon 7 1S1
- QCM DERIVATION 1S Mars 2010
- DV n ° 7 1S1 27 MARS 2010
- RESUME 3 COMPORTEMENT ASYMPTO.
- RESUME II COMPORT.. ASYMPTO.
- RESUME 1 COMPORTEMENT ASYMPTO.
- INFO EX4 SUJET COMMUN 1S
- INFO EX2 SUJET COMMUN 1S
- INFO EX 3 SUJET COMMUN 1S
- INFO QCM SUJET COMMUN 1S
- SUJET COMMUN 1S 2 AVRIL 2010
- INFO2 TEST DER-LIM 1S 27/03/10
- INFO TEST 1S1 27/03/10
- TEST DERIV-LIM 1S1 27/03/10
- INFO4 LISTE EX LIM-DERIV 1S
- INFO 3 LISTE EX LIM-DERIVE 1S
- INFO 2 LISTE EX LIM-DERIV 1S
- INFO 1LISTE EX LIM-DERIV 1S
- LISTE EX 1 S LIMITE-DERIVEE
- AIDE 4 DV n° 7 1S 27 mars 10
- AIDE 3 DV n° 7 1S 27 mars 10
- AIDE 2 DV n° 7 1S1 27/03/10
- AIDE 1 DV n° 7 1S 27 mars 10
Leçon 8 1S1
- INTERRO. LIMITES 1S AVRIL 10
- INTERRO. DERIV-LIMI 10/4/10 1S
- QCM LIMITES
- SUITES NUMERIQUES 14 /04/ 10
- INFO EX N°46 pour le 16/04/10
- EXERCICE N°47 pour le 16/04/10
- EXERCICE N°48 pour le 16/04/10
- EX n°46 n°47 n°48 1S SUITES
- NOTES DS COMMUN 1S 02/04/10
- INFO 1 INTERRO DERIV-LIM 1S
- INFO 3 INTERRO DERIV-LIM 1S
- INFO 2 INTERRO DERI-LIMI1S
- EX Suites 1S1 17 04/10
1S1 Leçon 9
- INFO 1 DV n° 7 1S 27 mars 2010
- INFO 3 DV n° 7 1S 27 mars 2010
- UTILISATION DES SUITES
- INFO EX III PROBA 1S
- EX III PROBA 1S
- INFO EX II PROB. 1S1
- EX II PROB. 1S1
- INFO EX PROBA 1S
- EXERCICE PROBA. 1S
- Année 2009 - 2010 1S
- 3 ième TRIM. 1S
- NOTES DS n ° 9 26/ 05 / 10
- INFO DS n° 9 1S1 26 MAI 2010
- DS n° 9 1S1 26 MAI 2010
- INFO UTILISATION :SUITES
- NOTES DS n° 8 1S
- QCM n° 3 SUITES NUMERI.1S
- QCM n° 2 SUITES NUMERI.1S
- AIDE DV n° 8 1S 28 mai 2M10
- DV n° 8 1S1 28/05/ 2010
- INFO 2 DS n° 8 12Mai 2010 1S1
- INFO 1DS n° 8 12 Mai 2010 1S1
- DS n° 8 12 Mai 2010 1S1
- EXERCICE 1S SUITES MAI 2010
- INFO 4 DV n° 7 1S 27 mars 10
- INFO 2 DV n° 7 1S 27 Mars 2010
- Remarque
1S TS BTS SUITES
- LISTE D'EX. SUITES BTS1
- Cours: SUITES NUMERIQUES 1S
- SUITE I CALCULATRICE TI 84
- INFO EX 4 LISTE 2 SUITES MAI
- EX BAC S 2004 SUITES
- LISTE 2 EX SUITES 1S MAI 09
- INFO EX1 SUITES ADJACENTES
- II SUITES GEOMETRIQUES
- INFO EX4 DS 10 1S MAI 09
- INFO EX BAC S 2004 SUITES
- INFO EX 2 LISTE 2 SUITES MAI
- Web SUR TI 84
- INFO EX 2 SUITES ADJACENTES
- LISTE 1 D'EXERCICES. SUITES
- INFO EX 5 DS 10 1S MAI 09
- EX BAC SUITE TS
- QCM n° 1 SUR LES SUITES
- INFO FEUILLE PROGRAMMEE SUITES
- INFO EX 3 SUITES ADJACENTES
- I I I SUITES ARITHMETIQUE
- DS n° 10 23 MAI 2009 1S
- INFO EX 3 DS 10 1S MAI 09
- INFO EX1 LISTE 2 SUITES MAI
- EX 1, 2 ,3 SUITES ADJACENTES
- INFO LISTE 1 EX SUITES
- COMPLEMENTS TS SUITE NUMERIQUE
- INFO EX1 DS10 1S MAI O9
- INFO EX 3 LISTE2 SUITES MAI
- INFO EX4 SUITES ADJACENTES
- INFO FIN liste 1 SUITES
- SUITES ADJACENTES TS
- SUITE 2 TI 84
- INFO EX 2 DS10 1S MAI 09
- Devoir n° 1 TS1 7 sept 2013
- INFO DV n° 1 TS1 7 sept 2013
- Cours Suites TS sept 2013
- FEUILLE D'EX n°1 SUITES TS1 SE
- INFO FEUILLE D'EX n°1 SUITES T
- FEUILLE D'EX n° 2 SUITE TS1 S
- TEST COURS SUITES TS
- INFO TEST COURS SUITES TS
- INFO FEUILLE D'EX n°2 SUITES T
- AIDE pour le DV n° 2 TS1 04
- Devoir n° 2 TS1 4 octobre 20
- INFO Devoir n° 2 TS1 4 octob
- FEUILLE D'EXERCICE n° 3 SUITE
- TEST SUITES TS OCT 2013
- DS n° 1 11 /10/13 TS1
- INFO 1 DS n° 1 11 /10/13 TS
- INFO 2 DS n°1 TS1 11 oct 2013
- TABLEAU D'HONNEUR DS n° 1 TS1
1S DERIVATION
- LISTE 1 D' EX . DERIVATION
- INFO EX. 3 DERIVATION 1S
- INFO DV n° 5 EX 7 DERIV 1S
- INFO LISTE 5 EX DERIV 1S
- INFO LISTE 4 EX 6 DERIV 1S
- INFO LISTE 4 EX DERI 1S
- LISTE 5 D'EX. DERIVATION 1S
- INFO DV n° 4 1S 29 NOV.
- LISTE 3 D'EX. DERIVATION 1S
- LISTE 4 D'EX. DERIVATION 1S
- INFO. EX 3 DS 3 1S 22 Nov
- INFO. EX 4 DS 3 1S 22 Nov
- INFO. EX 2 DS 3 1S 22 Nov
- INFO. EX 1 DS 3 1S 22 Nov
- QCM 1 DERIVATION 1S
- DV n° 4 1S DERIV. NOV.
- INFO LISTE 2 EX DERIV 1S
- LISTE 2 D'EX. DERIVATION 1S
- EX 3 DERIVATION 1S
- INFO LISTE 1 EX . DERIV . 1S
1S ANGLES, ARCS , ORIENTES OU NON
- INFO LISTE 1 EX ANGLE ORIEN
- LISTE 1 EX ANGLE ORIEN 1S
- ANGLES ORIENTES TRIGO
- DV n° 7 1S
- INFO DV n° 7 1S 9 Mars
- INFO EX 2 DS6 1S1 14 /2/ 09
- INFO EX1 DS n°6 14 /2/ 09
- EX TRIGO 1S Mars
- FORMULAIRE TRIGO
- DS n° 7 1S 1 14 FEV. 09
- INFO DS 7 1S1 14 Mars 08
- EX SIN ' cos '
- INFO EX SIN ' COS '
- I. ANGLE , ARC ORIENTE OU NON
1S PRODUIT SCALAIRE
- PROD . SCALAIRE 1 S Mars 09
- INFO LISTE1 PRO. SCA MARS 09
- RESUME PRODUIT SCALAIRE
- EX 12 PROD SCAL 1S AVRIL 09
- INFO 2 DV n° 7 1S 27 mars 10
- EX 13 PROD SCAL 1S AVRIL 09
- EX 14 PROD SCAL 1S AVRIL 09
- EX 15 PROD SCAL 1S AVRIL 09
- EX 16 PROD SCAL 1S AVRIL 09
- LISTE 2 PROD SCAL 1S AVRIL 09
- ACTIVITE PROD SCALAIRE
- INFO EX 11/ 04 /09 Stagiaire
- EX 11/ 04 /09 Stagiaire
- EX 04/04/09 stagiaire
- INFO EX 04/04/09 Stagiaire
- INFO EX2 DS9 1S 2 MAI 09
- INFO EX 1 DS 9 1 S 2 MAI 09
- INFO EX 3 DS 9 1 S 2 MAI 09
- INFO EX 4 DS 9 1 S 2 MAI 09
- INFO EX 5 DS 9 1S 2 Mai 09
- QCM n ° 1 PRODUIT SCALAIRE
- INFO 2 DV n° 7 1S 27 mars 10
- INFO 2 DV n° 7 1S 27 mars 10
- EX1 PROD SCAL 1S AVRIL 09
- LISTE 1 EX PROD SCAL MARS
- INFO EX 5 6 7 8 PROD SCALAIRE
- TRAVAIL 1S1 SAMEDI 28 MARS 09
- INFO ACTIVITE 28 MARS 09
- INFO 4 DS 1S1 04/04/09
- INFO EX 5 DS 1S1 04/ 04/ 09
- INFO EX1 DS 1S1 04/04/09
- Sujet Commun 1S 04 / 04 /09
- INFO EX 2 DS COMMUN 4/4/09 S
- INFO EX 3 DS COMMUN 4/4/09
- EX 11 PROD SCAL 1S AVRIL 09
- EX 2 PROD SCAL 1S Avril 09
- EX3 PROD SCAL 1S1 AVRIL 09
- EX4 PROD SCAL 1S1 AVRIL 09
- EX 5 PROD SCAL 1S AVRIL 09
- EX 6 PROD SCAL 1S AVRIL 09
- EX 8 PROD SCAL 1S AVRIL 09
- EX 7 PROD SCAL 1S AVRIL 09
- EX 9 PROD SCAL 1S AVRIL 09
- EX 10 PROD SCAL 1S AVRIL 09
1S LIMITES
- COMPORTEMENT ASYMPTOTIQUE 1S
- COMPORT. ASYMPTOTIQUE 1S
- ACTIVITE PRELIMI. LIMITES
- INFO EX 2 DS 5 1S J 09
- INFO EX 1 DS N° 5 1S 1
- DS N° 5 1S 1 24 janvier 09
- INFO DV6 1S JV 09
- INFO LISTE 2 EX LIMITES 1S
- INFO DV6 1S JV 09
- LISTE 2 D'EX LIMITES 1S
- INFO EX6 LISTE 1 1S LIMITES
- INFO EX7 LISTE 1 1S LIMITES
- INFO EX 5 LISTE 1 1S LIMITE
- INFO LISTE 1 EX 1 . 2. 3 . 4
- INFO EX2 DS4 1S 20 Déc.08
- INFO EX3 DS4 1S 20 Déc 08
- INFO EX 1 DS4 1S 20 Déc 08
- EX LIMITES 1S Janv. 09
- COMPORT. ASYMPTOTIQUE 3 1S
1ES Devoir et Exercices
- DS n° 6 1ES - L 11 février 2
- INFO DS n° 6 1ES-L 11février
- DEVOIR MAISON 1 ES- L 28/01/1
- DEVOIR MAISON 28/01/1012
- INFO DS 1 ES 17 /12/11
- DS 1ES DS 2 17 / 12/
- INFO DV MAISON 1ES-L 17/12
- DV MAISON 1ES-L 17/12/11
- DV maison 1ES Samedi 2 déc. 20
- INFO DV maison 1ES-L Samedi 2
- INFO DV n° 2 Maison du 12 nov.
- INFO DS n °3 1ES-L
- DS n° 3 1 ES-L 07/11/11
- EX n° 22 Livre 1ES Hyperbole
- INFO Ex n° 27 page 106
- INFO DS 1ES 29 MAI 2010
- TD de programmation linéaire
- DS n° 1 1ES 10/10/09
- INFO DS n° 1 1ES 10 / 10/09
- DS n° 2 23 / 10 / 09 1ES
- INFO DS n° 2 23/10/09 1 ES
- DS n° 3 1ES 17/11/09
- INFO DS n°3 1ES 17/11/09
- DS 6 avril 2010 1 ES
- INFO DS 6 AVRIL 2010 1 ES
- DS 1ES 29 MAI 2010
- INFO TEST 3 1ES 17 / 11/10
- INFO TEST 1 1ES 29/09/10
- TEST 1 1ES 29/09/10
- TEST 3 1ES 17 / 11/ 10
- INFO TRAVAIL 1ES SEPT 2011
- TRAVAIL 1 1ES SEPT 2011
- COEFFICIENT MULTIPLICATEUR
- TEST 1ES SUITES MARS 2011
- INFO DS 1ES 23/11/10
- DS 1ES 23 / 11/10
1S 1ES TS BTS PROBA.
- EXERCICE 1ES SUR : LOI BINOMIA
- LISTE 1 EX PROBA. BTS1 nov
- INFO LISTE 2 EX . PROB BTS1
- LISTE 2 D'EX. PROB BTS1
- INFO TEST PROBA Fév. 2011
- PROJET 2 BTS1 EX 1
- INFO TRAVAIL BTS MARS 2011
- PROJET 2 BTS1
- EX PROB TS
- INFO 4 TEST PROBA 11 mars 2011
- INFO 3 TEST PROBA 11 mars 2011
- INFO 2 TEST PROBA 11 mars 2011
- INFO 1 TEST PROBA 11 mars 2011
- TEST PROBA 11mars 2011
- TEST PROBA Fév. 2011
- INFO LISTE 1 D' EX PROB BTS1
- INFO TEST 9/2/11 BTS PROB
- TEST PROB Février 2011
- INFO TRAV SUR ORDI JV 09
- INFO TEST ORDI JV 09
- TEST SUR ORDI BTS JV 09
- TRAVAIL SUR ORDI BTS JV 09
- INFO INITIATION VAR BTS1
- INITIATION AUX V.A.R BTS1
- LISTE 3 D'EX BTS1 PROBA.
- INFO LISTE 3 EX PROB. BTS1
BTS1 LOGIQUE
- LOGIQUE ELEMENTAIRE
- LOGIQUE ELEMENTAIRE 1
- LOGIQUE ELEMENTAIRE 2
- Devoir 1 BTS Logique
- INFO DV 1 BTS1 OCT.09
- TEST 2 LOGIQUE BTS1 A 17/10/11
- INFO TEST 2 LOG BTS1 A 17/10/
- INFO TEST 2 LOG BTS1 B 21
- TEST 2 LOG BTS1B 21/10/1
- D. AVAKOV : 09/10
- QCM DE LOGIQUE
- EXERCICES DE LOGIQUE
- EXERCICES DE LOGIQUE DE BASE
- INFO EX DE LOGIQUE DE BASE
- QCM DE LOGIQUE 3
- TEST n°6 LOGIQUE
- INFO TEST n° 6 LOGIQUE
- TEST n ° 7 LOGIQUE BTS 1
- INFO TEST n ° 7 LOGIQUE
- CORRECTION DES EX.
- CONTRÔLE TEST 1
- CORRECTION TEST 1
- Contrôle TEST 2 Logique
- INFO . Contrôle TEST 2
- LISTE D' EXERCICES 2 LOGIQUE
- INFO LISTE 2 EX LOGIQUE BTS
- TEST 3 LOGIQUE BTS TS
- TEST n° 5 LOGIQUE
- INFO TEST n° 5 LOGIQUE
- INFO TEST n° 4 LOGIQUE
- TEST n°4 LOGIQUE
- Bases du Second degré
- INFO ACT. Types Raisonnements
- ACTIV: Types de raisonnements.
- INFO TEST 3
- TEST Logique BTS
- INFO TEST Logique
- TEST DE LOGIQUE 15/11/2005 BTS
- INFO TEST DE LOGIQUE 15/11/200
- Exercices de logique
- TEST LOGIQUE BTS1 8/10/14
- INFO TEST LOGIQUE BTS1 8/10/
- TEST 15 octobre 2014
- INFO TEST LOGIQUE 15 /10/14
- TEST 2 LOGIQUE BTS1 A 5/11/14
- INFO TEST LOGIQUE 5 / 11 / 14
- Compléments
- Bijection: surjection: injecti
- E22
- CONVOCATIONS E 22
BTS1 ALGEBRE DE BOOLE
- ALGEBRE DE BOOLE RAPPELS
- DS BTS 1 A SLAM 07/02/
- ALGEBRE DE BOOLE 1
- INTRO. TERTIAIRE ALG. DE BOOLE
- LISTE 1 D' EX . ALGEBRE DE B
- DS n° 1 BTS1A 23/10/09
- INFO DS 13/2/09 BTS1A
- TRAVAIL 3 ORDI BTS FV 09
- INFO TEST ALG.BOOLE 12/11/2010
- INFO LISTE 1 EX ALG BOOLE
- INFO 1 DS n°1 BTS1A 23/10/09
- Proposition ex par BTS1A
- TRAVAIL 4 ORDI BTS FV 09
- TEST ALG. DE BOOLE 12/11/10
- TEST ORDI BTS BOOLE
- INFO 2 DS n°1 BTS1A 23/10/09
- INFO DV n° 1 12 oct. 09 BTS
- INFO TRAVAIL 2 ORD BTS FV 09
- TRAVAIL SUR ORDI BTS FV9
- QCM ALGEBRE DE BOOLE
- Ex extrait d'un sujet de BTS
- INFO TRAVAIL 4 ORD BTS FV 09
- EX ALGEBRE DE BOOLE
- TEST ALG. DE BOOLE 2010
- TRAVAIL 2 ORDI BTS FV 09
- INFO TRAVAIL ORDI BTS FV9
- INFO DS n° 1 BTS1B 20/10/09
- DS n° 1 BTS1B 20 / 10 / 09
- INFO TRAVAIL 3 ORD BTS FV 09
- EXERCICE BTS1 B 30 novembre
- INFO EX 2 TEST BTS1 B 30 nove
- INFO EX 1 TEST BTS1 B 30 novem
- EX 3 BTS1B Décembre 2012
- INFO EX3 TEST BTS1 décembre 20
- TEST n° 2 13novembre 2013
- INFO TEST n°2 13 novembre 2013
- INFO TEST n° 2 du 18 novembre
- TEST n° 2 du 18 novembre 2013
- TEST n° 3 mercredi 20 nov. 201
- INFO TEST n° 3 mercredi 20 no
- INFO TEST n°3 26 novembr
- TEST n°3 26 novembre 2013
- INFO TEST ALG DE BOOLE 11 déc.
- TEST ALG BOOLE 11 déc. 201
- INFO TEST BTS1 A 26 NOV 2014
- INFO TEST BTS1 du 3 décembre
- BULLETIN sem1 dec 2014 BTS1A
- BULLETIN sem1 dec 2014 BTS1B
- INFO EXERCICE 3
- EXERCICE 3
- TEST 1 12 octobre 2016
- DS 1 12 octobre 2016
BTS1 MATRICES et SYSTEMES LINEAIRES
- CALCUL AVEC DES MATRICES
- ACTIV 1 ORDI MATRICES BTS
- INFO EX 3 SYSTEME LINEAIRE
- TEST GRAPHE BTS1
- INFO EX4 SYSTEME LINEAIRE
- EX SUR LES GRAPHES
- INFO EX GRAPHE
- ACTIVITE GRAPHES ORIENTES
- INFO ACTIVITE GRAPHE
- EX GRAPHE 1
- INFO EX 1 GRAPHE
- INFO TEST
- TEST MATR.-SYST. nov 09
- INFO TEST 20/11/09
- TEST 2 MATR.-SYST. nov 09
- INFO TEST2 MATR. SYST. NOV 09
- TEST MATR.-SYST.GRAPHE déc. 09
- INFOTEST DEC 09 MATRICE-GRAPHE
- INFO TEST BTS1A 1/12/09
- EX SUJET : SYST. MATR. BTS
- EX DE SUJET BTS MATRICE- SUITE
- INFO EX SUJET BTS MATR. SUITE
- TI 84 et MATRICES
- TEST BTS1 MATRICES 2010
- INFO EX1 SYSTEME LINEAIRE
- ACTIV. SYSTEME LINEAIRE BTS
- INFO ACTIV 1 ORDI MATRICES
- EX 0 EPREUVE DE BTS MATRICES
- INFO EX 0 EPREUVE BTS MATRICE
- SYSTEME EQUATIONS LINEAIRES
- EX 2 EPREUVE DE BTS MATRICES
- INFO EX2 EPREUVE BTS MATRICE
- EX 3 EPREUVE DE BTS MATRICES
- INFO EX3 EPREUVE BTS MATRICE
- ACTIV.2 ORDI MATRICES BTS
- ACTIV 4 ORDI MATRICES BTS
- EXERCICE : SYST. LIN Nov 09
- LISTE A D' EX. SYST. 10/11/09
- INFO LISTE A EX SYST. 10/11/9
- EX1 SYSTEME LINEAIRE
- EX4 SYSTEME LINEAIRE
- EX2 SYSTEME LINEAIRE
- EX3 SYSTEME LINEAIRE
- INFO EX 5 SYSTEME LINEAIRE
- INFO EX 2 SYSTEME LINEAIRE
- ACTIV.3 ORDI MATRICES BTS
- TEST BTS1B 29/03/13
- INFO TEST BTS1A 11 déc 2013
- TEST MATRICE BTS1 A
- SEMESTRE 1_ 2013 BTS1A
- TEST MATRICES 18 /12/13
- INFO TEST 18/12/13
- INFO EXERCICES 3 bis
- EXERCICE SYST 26 Nov 2014
- EXERCICE sur les matrices et s
- TEST BTS 1 du 3 février 2016S
- INFO TEST 3 Février 2016
- INFO TEST n°2 BTS1 B 17 fév
- INFO TEST n°2 BTS 1 A 17 févri
- TEST n° 2 BTS1 A 17 février 20
- TEST n°2 BTS 1 B 17 février 20
BTS1 SUJETS
- SUJET 2009 BTS
- INFO EX 1 SUJET 2009 BTS
- ALERTE BTS SESSION 2009
- EX3 BTS SESSION 2009
- INFO EX2 A BTS SESSION 2009
- INFO EX2 B BTS SESSION 2009
- INFO EX 2 C BTS SESSION 2009
- BTS SIO 2017 sujet
- INFO SUJET BTS SIO 2017
- INFO Maths.approfondies ex 1 B
- Sujet Math.approfondies BTS SI
- INFO Maths.approfondies ex 2 B
BTS1 GRAPHE ORIENTE 2
- INFO EX 00 SUR LES GRAPHES
- EX 00 SUR LES GRAPHES
- LISTE EX SUR LES GRAPHES
- INFO EXGRAPHE EPREUVE BTS FR0
- DS BTS1 B 10 AVRIL 09
- EX III SUR LES GRAPHES
- TEST GRAPH BTS Déc. 2010
- INFO EX III SUR LES GRAPHES
- INFO TEST GRAPH Déc. 2010
- DS BTS1 10 Avril 2009
- INFO LISTE EX SUR LES GRAPHES
- INFO DS 10 AVRIL 09 BTS1A
- EX GRAPHES EPREUVE BTS FR00
- INFO DS BTS1B 10 AVRIL 09
- TEST GRAPHES janvier 2014 BTS
- INFO TEST GRAPHE janvier 2014
- TEST2 GRAPHE 28 janvier 2014
- INFO TEST 2 28 janvier 2014
- TEST 5 GRAPHE BTS 2014
- INFODEBUT TEST 5 GRAPHE BTS
- TEST 6 GRAPHE BTS1 janvier 14
- INFO TEST 6 GRAPHE BTS1 janvie
- TEST BTS1B 21 janvier 2015
- INFO TEST BTS1 B 21 janvier 20
- TEST BTS1 A mercredi 21 janvie
- TEST BTS1 A 4 février 2015
- INFO TEST BTS1 A 4 février 201
- INFO EX 2 TEST BTS1A janvier
- EX1 TEST BTS1 B 11 février 20
- INFO EX1 TEST BTS1 B 11 févri
- EX2 TEST BTS1 B 11 février 201
- INFO EX2 TEST BTS1 B 11 févri
- Sujet Nouvelle calédonie
BTS1 VARIABLES ALEATOIRES
- PROBA: VARIABLES ALEATOIRES 1
- PROBA: VARIABLES ALEATOIRES 2
- V.A.R. DE LOI NORMALE
- INFORMATION EXERCICES
- EX 1 DU SUJET 2003
- INFO TEST 5 SUR V.A.R
- CORRECTION EX: LOIS NORMALES
- INFO LISTE EX . VAR.
- INFO TEST 4
- Contrôle TEST STAT. PROBA.
- INFO TEST 3
- INFORMATION EX 1 SUJET 2003
- EXERCICES ( LOI S NORMALES. )
- EX 3 BTS SUJET 2000
- EXERCICES SUR LES V.A.R
- TEST V.A.R 4
- TEST 5 V.A.R
- INFO TEST 2 PROBABILITE
- LISTE EX . VAR
- QCM 1
- LISTE 2 EX . LOIS NORM.
- Contrôle TEST 3
BTS1 DENOMBREMENTS
- EX. 1 SUR LES DENOMBR.
- EX 2 SUR LES DENOMBR.
- EX 4 SUR LES DENOMBR.
- INFO TEST BTS1 15 / 02/10
- TEST BTS1A 26/01/10
- INFO EX1 TEST BTS 1 26/01/10
- INFO EX2:TEST BTS 1 26 janv10
- INFO EX4 TEST BTS1 26 JANV
- INFO EX3 TEST BTS1 26 JANV
- DV BTS1 5/ 02 / 10
- INFO DV BTS1 5 février 210
- TEST BTS 2010
- TEST BTS1 DENOM-PROB f 2008
- INFO TEST BTS1 16/02/10
- TEST BTS1 DENOM-PROB 16/2/2010
- INFO TEST DENO-PRB BTS 16/2/10
- INFO EX4 BAC S JUIN 2010
- TEST BTS1 26/01/11
- INFO TEST BTS 1 26/01/11
- DS-TEST BTS1 22/01/2010
- DENOMBREMENTS 1
- PROBLEMES DE DENOMBR.
- INFO PROBLEMES DENOMBR. BTS
- DS 2 BTS1B 19 nov 0 8
- INFO DS 2 BTS1B 19 NOV. 08
- LISTE 2 D'EX. DENOMBR. BTS
- INFO LISTE2 EX DENOMB BTS
- DS 2 BTS1A 28 nov 08
- INFO EX1 DS 2 BTS1A 28 NOV.
- INFO EX 3 ; 4 ; 5 DS2 BTS1A
- INFO EX 2 DS2 BTS1A
- INTERRO. COURS. BTS1 DENOMBRE
- INFO INTERR. COURS DENOMB.
- INFO DS BTS1 22/01/20010
- REMARQUE DS BTS1 22/1/10
- Nombre de combinaisons à l'aid
- COMPLÉMENTS SUR LES DENOMBREM
- COMBINAISONS AVEC RÉPÉTITIONS
- INFO COMBINAISONS AVEC RÉPÉTI
SPE MATHS TS 2016 -2017
- INFORMATION SUR LE BINÔME DE N
- TEST n° 2 MATRICES Spé maths
- INFO TEST n° 2 MATRICES Spé
- Notes TEST N ° 2
- DV n° 2 TS spé maths
- INFO DV n ° 2 TS spé maths
- FEUILLE D'EXERCICES sur les g
- SUITE DE LA FEUILLE D'EX sur
- Notes TEST N ° 3
- INFO TEST n° 3 Spé maths TS
- TEST n° 3 Spé maths TS
- Remarque devoir maison n°4
- DV n °4 TS Spé maths déc.2015
- INFO Devoir maison n°4 TS s
- Remarque
- EXERCICE 1 : restes et con
- EXERCICE 2 sur les congruenc
- EXERCICE 3 sur les congruences
- EXERCICE 4 sur les diviseurs.
- DV du 26 janvier reporté au 2
- EX spé 09/ 02/16
- INFO EXERCICE spé
- Bac Blanc 16 février 2016
- DEVOIR DU 22 MARS 2016
- INFO DEVOIR 22 mars 2016
- TEST 29 mars 2016
- INFO TEST du 29 mars 2016
- Notes bac blanc. 14 mai 2016
- INFO EX1 DV spé maths sept
- EX2 DV spé maths sept 2016
- EX1 DV spé maths sept 2016
- INFO EX2 DV TS spé maths
- TEST n° 1 mardi 4 octobre 2016
- Entraînement 4 oct 2016
- TEST n° 2 mardi 18 octobre 2
- INFO Test n ° 2 Mardi 18 octo
- INFO DV n° 2 mardi 18 octob
- Devoir maison n°2 Mardi 1
- TEST n° 3 mardi 8 novembre 2
- INFO TEST 3 mardi 8 nov 201
- TEST 4 22 nov 2016
- INFO TEST 22 novembre 2016
- INFO Devoir 3 22 nov 2016
- DV 4 Spé maths 8 / 12/16
- INFO DV n ° 4 Spé Maths TS
- TEST 5 10 janvier 2017
- INFO TEST 5 10 janvier 2017
- INFO DV n° 5 TS spé 24 janv
- DV 5 du 24 janv. 17 TS spé
- INFO TEST EX1 spé TS 31/1/17
- TEST EX1 spé TS 31 janvier 20
- INFO TEST EX 2 TS spé 31 jan
- TEST EX2 spé TS 31 janv.2017
- DV n° 6 TS spé 28/02/17
- INFO DV n° 6 TS spé 28/02/
- Sujet Bac Blanc 24 février 21
- INFO BAC BLANC 24 fev.2017 spé
- TABLEAU D'HONNEUR
- DV n° 7 TS spé 14/03/17
- INFO DV n° 7 TS spé 14 mars
- Activité carte vitale
- INFO Activité carte vitale
- Activité code barres EAN 13
- INFO activité code barres
- Activité : Chiffrement de VIGE
- INFO activité chiffrement de V
- Nombre de Mersenne.. Nombre pa
- INFO Nombres de Mersenne.Nombr
- INFO TEST TS spé math du 21 ma
- TEST TS spé math du 21 mars 2
- EX sur les ROCS TS spé maths
- INFO EX sur les ROC TS spé ma
- INFO DV n° 8 TS spé du 18 avr
- DV n°8 TS spé math. 18 / 04/1
- INFO ACTIVITE : CARMICHAËL
- ACTIVITE : CARMICHAËL TS
- Petit Th. de Fermat TS spé ma
- INFO Activité: Petit th.de Fer
- INFO :Activité de dem.du petit
- Activité de dem.du petit th de
- INFO EX SPE BAC BLANC du 4 m
- EX Spé Math.TS Bac Blanc 4 ma
- Notes ex 4 bac blanc 4 mai 201
- EX de bac spé S 2017 N.
- FEUILLE D'EX TS spé maths mai
- INFO TEST TS spé maths du 16
- TEST TS spé maths du 16 mai 20
BTS1 NUMERATION
- Cours : numération
- FEUILLE D'EXERCICE sur la numé
- Feuille d'exercices sur la num
- COMPLEMENT A 2
- ENTIER RELATIF EN BASE 2
- TEST 1 NUMERATION BTS1 B
- INFO TEST 1 B_NUMERATION
- TEST BTS1 NUMERATION
- INFO TEST BTS1 NUMERATION
- TEST n° 1 BTS septembre 2011
- EXERCICES DE NUMERATION
- INFO 2 FEUILLE EX NUMERATION
- INFO FEUILLE EX NUMERATION
- FEUILLE EX NUMERATION
- BASE : SYSTEME DE NUMERATION
- ENTIERS NEGATIFS EN BASE 2
- SOMME ET PRODUIT EN B 2
- INFO NUMERATION TRAVAUX BTS1
- NUMERATIO: TRAVAUX A EFFECTUER
- Résumé de cours de numération
- CONVERSION BASE 10 VERS BASE B
- essai
- EX DE NUMERATION BTS1
- INFO EX BTS1
BTS1 ALGORITHMIQUE
- PYTHON.2 FEUILLE D'EX 9
- PYTHON. 2 FEUILLE 4 D'EXER
- RESUME: Python 2.7 utile pour
- FEUILLE D'EX n° 9 bis Dichoto
- PYTHON. 2 INFO Feuille 4
- PYTHON.2 INFO FEUILLE n° 9 D'E
- PYTHO 2.7 RENTREE BTS ALGORIT
- DEBUT en Python.2
- PYTHON 2. FEUILLE n° 9 TER
- PYTHON.2 Feuille 10 :Sujet EXA
- TEST ALGO BTS1B 24 nov. 2014
- Python 2 : Deux modules
- PYTHON 2 INFO FEUILLE 7 EX
- PYTHON 2 FEUILLE n° 10 BIS
- PYTHON. 2 Feuille 1 EX
- PYTHON 2 :Feuille n°5 sur les
- PYTHON .2 FEUILLE n° 3 d'exer
- PYTHON 2.7 TEST BTS1B 4/12/
- BTS1B TEST ALGO 17 nov 2014
- Pyrthon 2 Feuille n° 6 d'exer
- PYTHON .2 FEUILLE n° 2 D'E
- BTS1A TEST ALGO déc.. 2014
- PYTHON.2 FEUILLE D'EX n° 8
- PYTHON. 2 Feuille n°9 QUARTO
- PYTHON. 2 INFO Feuille n° 8 bi
- PYTHON .2 INFO. FEUILLE n°3
- PYTHON 2 FEUILLE n° 7 EX
- PYTHON. 2 INFO Feuille 1 EX
- INFO TEST ALGO BTS1 A déc. 201
- INFO PYTHON 2.7 TEST BTS1B
- PYTHON 2. FEUILLE n° 7 BIS
- PYTHON .2 FEUILLE n° 3 BIS
- PYTHON.2 INFO FEUILLE 10 Sujet
- PYTHON.2 INFO FEUILLE n° 8 D'E
- INFO TEST ALGO 24 nov 2014
- PYTHON 2.7 QUESTIONS
- INFO BTS1 B TEST ALGO 17 nov 2
- PYTHON.2 INFO FEUILLE 2
- PYTHON 2.7 TEST BTS1 11/
- INFO PYTHON 2.7 TEST BTS1 11/1
- PYTHON 2.7 TEST BTS1A 10
- INFO PYTHON 2.7 TEST BTS1A 10
- TEST BTS1 B 1 mars 2017
- TEST BTS1 26 janvier 2016
- PYTHON. 2 PREMIERS EXEMPLES
- PYTHON 2 FEUILLE n° 11 D'EXERC
- PYTHON 2 FEUILLE n° 11 bis D'E
- PYTHON.2 INFO Feuille n°11 D'
- PYTHON 2.7 TEST BTS1A 17/12/
- INFO PYTHON 2.7 TEST BTS1 A 1
- TEST ALGO BTS 28/1/14
- INFO TEST ALGO BTS 28/1/14
- PYTHON 2 INFO FEUILLE n° 12
- PYTHON 2 :Feuille n°12 D'EXERC
- TEST ALGO 5 février 2014
- INFO TEST D'ALGO 5 février 201
- PYTHON 2 FEUILLE n° 13 D'EXERC
- PYTHON.2 INFO FEUILLE n° 13 D
- PYTHON.2 FEUILLE n ° 14 D'EX
- PYTHON.2 INFO FEUILLE n °14 D'
- Python 2 FEUILLE n°15 D'EXERCI
- PYTHON 2 INFO FEUILLE n° 15 D'
- PYTHON.2 FEUILLE n° 16
- PYTHON.2 INFO FEUILLE n°16 D'E
- PYTHON.2 INFO FEUILLE n°17 D'E
- PYTHON.2. FEUILLE n°17
- PYTHON.2 FEUILLE n° 18 D'EXERC
- PYTHON.2 INFO FEUILLE n°18 D'E
- FEUILLE D'EXERCICE n° 19 BTS1
- QCM
- PYTHON.2 INFO FEUILLE n° 19
- TEST ALGO 10 février 2016
- INFO TEST ALGO du 10 février 2
- PYTHON.2 FEUILLE n° 20 D'EXERC
- PYTHON.2 INFO FEUILLE n ° 20
- Entraînement d'algo mardi 8
- INFO Entraînement d'algo. mard
- Entraînement d'algo 9 / 4/14
- INFO Entraînement d'algo. merc
- PYTHON.2. INFO FEUILLE n° 21 B
- PYTHON.2. FEUILLE n° 21 D'EXE
- PYTHON.2. FEUILLE D'EX n°22 BT
- PYTHON.2. INFO FEUILLE n° 22 D
- PYTHON.2 FEUILLE n° 23 D'EX
- PYTHON.2.INFO FEUILLE n° 23 D'
- PYTHON.2. FEUILLE n° 24 D'EX
- PYTHON .2 .INFO FEUILLE n° 24
- PYTHON 2 FEUILLE n° 24 bis su
- PYTHON 2.7 FEUILLE n° 24 Ter
- PYTHON 2 FEUILLE n° 24 quatr
- PYTHON 2 FEUILLE n° 24 quinto
- PYTHON 2 FEUILLE n° 24 six s
- PYTHON 2 FEUILLE n° 24 sept
- PYTHON 2 FEUILLE n° 24 hu
- PYTHON 2 FEUILLE n° 24 neu
- PYTHON 2 FEUILLE n° 24 di
- PYTHON 2 FEUILLE n° 24 11
- PYTHON 2 FEUILLE n° 24 dou
- PYTHON 2 FEUILLE n° 24 tr
- PYTHON 2 FEUILLE n° 24 qu
- PYTHON.2. FEUILLE n° 25 D'EXER
- PYTHON. 2 INFO FEUILLE n° 25
- PYTHON.2.. FEUILLE n° 26 D'EXE
- PYTHON.2.INFO FEUILLE n ° 26 D
- PYTHON.2. FEUILLE n° 27 D'EXER
- PYTHON INFO FEUILLE n° 27 D'EX
- PYTHON.2 FEUILLE n° 28 D'EXE
- PYTHON.2.INFO FEUILLE n° 28
- PYTHON.2 INFO FEUILLE n° 29 D
- PYTHON.2 FEUILLE n° 30 D'EX B
- PYTHON 2. FEUILLE n°31 Matrice
- PYTHON 2. FEUILLE n°32
- PYTHON. 2 FEUILLE n°33
- PYTHON. 2 FEUILLE n°34 d'EX A
- Sous suites convergentes de (s
- PYTHON 2 FEUILLE n°36
- PYTHON 2 FEUILLE n° 37
- IIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIII
- PYTHON. 2 Généralités
- PYTHON. 2 EXEMPLES BASIQUES
- PYTHON.2 COURS D'ALGORITHM
- PYTHON PROCESSUS DE PROGRAMM
- PYTHON. 2 LIEN VERS UN TUTORI
- PYTHON. 2 TEST
- PYTHON .2 TUTORIEL EN FRANCAIS
- PYTHON . 2 RESUME SUR LISTES
- Python . 2 : LISTE
- PYTHON 2 LISTES PAR L'EXEMPLE
- Cours PYTHON 2ou3
- PYTHON.2 TEST 2 EXAMEN BTS 1
- PYTHON.2 INFO TEST 2 EXAMEN BT
- PYTHON. 2 : PYTHON-ALGOBOX COM
- PYTHON2 EX proposé par Tony
- Lien vers les Modules disponib
- IIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIII
- CCF E22 n°8 BTS 1 SIO mai 2
- CCF E22 n°2 BTS 1 SIO mai 2
- CCF E22 n° 1 BTS 1 SIO Mai
- Première page d'un sujet de l'
- ALGO DIRECT
- ALGO DIRECT2
- ALGO TERTIAIRE ALGOBOX
- TEST ALGO n° 1 BTS 1
- TEST 2 AGLO BTS 1
- INFO TEST ALGO n° 2 BTS1
- CONSEIL:REDACTION D'UN ALGORIT
- TEST SIO MARS
- CCF E22 n°4 BTS 1 SIO mai 2
- INFO DECOMPOSITION EN FACTEURS
- ALGO DIRECT3
- INFO TEST 1 ALGO BTS1
- INFO LISTE 4 EX ALGO
- EVALUATION D'UN ALGORITHME D'U
- EX ALGO
- INFO LISTE 3
- INFO LISTE 2 EX ALGO
- LISTE 1 D'EX ALGORITHME
- EX4 ALGORITHME
- EX 5 D'ALGORITHME
- EX 3 D'ALGORITHME
- EX 2 D'ALGORITHME
- EX 1 D'ALGORITHME
- INFO LISTE1 EX 3 ; 4 ; 5 ALGO
- CHARGEMENT D'ALGOBOX
- Ecran ALGOBOX
- INFO EX 5 D'ALGO: DECIMAL vers
- LISTE 4 EX ALGO
- INFO EX 4 ALGORITHME
- INFO EX 3 D'ALGORITHME
- LISTE 3 D'EX ALGORITHME
- INFO EX 2 D'ALGORITHME
- INFO LISTE 2 EX ALGORITHME
- LISTE 2 D'EX ALGORITHME
- INFO EX 1 ALGORITHME
- INFO LISTE1 EX 1 ET 2 ALGO
- EQUATION 2ième DEGRE ALGOBOX
- COURS3 D'ALGORITHMIQUE BTS SIO
- COURS 1 BASIQUE D'ALGORITHMIQU
- COURS 2 BASIQUE D'ALGORITHMIQU
- Feuille 1d'ex.algo."papier
- Feuille 2 d'ex. algo. "papier"
- ALGO permutation circulaire 8
- TEST1 ALGO BTS
- INFO TEST ALGO EX1 27 nov 2012
- INFOTEST ALGO EX2 27 nov 2012
- INFO TEST ALGO EX3 27 nov 2012
- INFO TEST ALGO EX4 27 nov 2012
- INFO TEST ALGO EX5 27 nov 201
- INFO TEST ALGO EX 6 27 nov 20
- INFOTEST ALGO EX7 27 nov 2012
- INFO TEST EX8 BTS1A 27 novembr
- EXERCICE BTS 2011
- INFO EX1 TEST BTS1B 7 déc.2012
- INFO EX2 TEST BTS1B 7 déc 201
- INFO EX3 TEST BTS1B ALGO 7 d
- INFO EX4 TEST BTS1B 7/12/12
- INFO EX5 TEST BTS1B 1LGO 7/12/
- Division euclidienne par soust
- AIDE POUR RECUPERER UNE PARTIE
- TEST ALGO février 2015
- TEST ALGO2 février 2015 et jan
- LE CARRE DE POLYBE
- BTS1 Feuille n° 53
- TEST BTS1 1789
- INFO TEST BTS1 1789
- Proposé par wiliam
- Proposé par zndy
- EX proposé par Guillaume BTS1
- EX sur une idée d'un étudiant:
- Exercice2413
- 424
- METHODE du PIVOT de GAUSS
- Codage de HILL
- TEST ALGO
- Encoding
- SUJET 43 mai 2017
- SUJET 44 mai 2017
- SUJET 45 mai 2017
- SUJET 46 mai 2017
- SUJET 47 mai 2017
- SUJET 48 mai 2017
- SUJET 49 mai 2017
- SUJET 50 mai 2017
- SUJET 51 mai 2017
- SUJET 52 mai 2017
- SUJET 53 mai 2017
- SUJET 54 mai 2017
- SUJET 55 mai 2017
- SUJET 56 mai 2017
- SUJET 57 mai 2017
- SUJET 58 mai 2017
- SUJET 59 mai 2017
- SUJET 60 mai 2017
- SUJET 61 mai 2017
- SUJET 62 mai 2017
- SUJET 63 mai 2017
- SUJET 64 mai 2017
- SUJET 65 mai 2017
- SUJET 66 mai 2017
- SUJET 67 mai 2017
- SUJET 68 mai 2017
- SUJET 69 mai 2017
- SUJET 70 mai 2017
TS NOMBRES COMPLEXES
- INFO DS n° 3 TS2 14 nov 2011
- TEST TS NOMBRES COMPLEXES
- INFO TEST 1 TS2 NB COMLEXES
- TEST RAPIDE TS NB COMPLEXES
- DS n° 3 TS2 14/11/11
- LISTE EX NOMBRES COMPLEXES
- EX FAIT LE 19 OCT 2010 TS2
- INFO DS n°2 Nb Compl 22/10/10
- INFO DS n° 3 TS2 12/11/10
- DV n° 3 TS2 15/11/10
- Réponse à une question posée
- AIDE DV n ° 3 TS2 15 /11/10
- DV n° 2 TS2 1 8 / 10 / 10
- SITUATION AVEC NB COMPLEXES
- INFO DV n° 3 TS2 15/11/10
- INFO DV 2 MAISON TS2 OCT 10
- TEST NB COMPLEXES
- Réponse à une question posée
- DS n°2 Nb Complexes 22/10/10
- INFO TEST NB COMPLEXE
- DS n° 3 TS2 12/11/10
- INTRO NOMBRES COMPLEXES
- Leçon n° 1. Nombres complexes
- EXTRAIT D'EXERCICE DE BAC. Nb
- INFO EXTRAIT D'EX BAC
- PREMIER TRAVAIL A REALISER
- SECOND TRAVAIL à réaliser
- INFO SECOND TRAVAIL
- TROISIEME TRAVAIL A REALISER
- INFO TROISIEME TRAVAIL
- Suite 1 du cours: Nb Complexes
- Suite 2 du cours: Nb Complexes
- Suite 3 du cours: Nb Complexes
- Suite 4du cours:Nb Complexes
- Suite 5 du cours: Nb Complexes
- Suite 6 du cours:Nb COMPLEXES
- Suite 7 du cours: Nb COMPLEXES
- TEST 1 Nb COMPLEXES
- INFO TEST 1 Nb COMPLEXES
- TABLEAU D'HONNEUR TS2
- Devoir maison 1 du 24/09/10 TS
- AIDE1 DV n° 1 TS 24 sept 2010
- AIDE 2 DV n° 1 TS 24 sept 2010
- DS 1. 4/10/10 TS
- INFO DS n°1 6/10/10
- FEUILLE 1 D' EX. NOMBRE COMPLE
- INFO 1 FEUILLE 1 D'EX
- INFO 2 FEUILLE 1 EX NOMB. COMP
- INFO 3 FEUILLE 1 EX NOMB. COMP
- FEUILLE 2 D' EX. NB COMPLEXE
- LISTE 3 D'EX Nb COMPLEXES
- INFO 1 Liste 3 EX Nb COMPLEXES
- INFO 2 LISTE 3 EX Nb COMPLEXES
- INFO 3 LISTE 3 EX Nb COMPLEXES
TS DERIVATION DE COMP. DE FONCTIONS
- ALGO EULER POUR LA COURBE D'UN
- NOTES TS2 B BLC
- DS n°5 TS2 EX 4 BAC BLC 12
- DS n° 4 TS2 17 décembre 20
- INFO DS n° 4 TS2 17/12/11
- INFO EXERCICE TS2 16 /12/1
- INFO EX 77 DV maison TS2 05
- INFO EX 31 DV maison TS2 05
- INFO EX 36 DV MAISON TS2
- INFO EX 78 DV maison TS2 05
- EULER : PRGM TI 84
- ALGORITHME DONNANT AVEC EULER
- COURBE DE EXP AVEC ALGOBOX
- METHODE D'EULER POUR EXP AVEC
- INFO LISTE 1 D' EX DERIV. DE
- LISTE 2 D'EX DERIV. COMPOSEE
- INFO LISTE 2 D'EX DERIV. COM
- LISTE 1 D' EX. DERIV. DE COMPO
- METHODE D'EULER POUR EXP
TS...........Leçon n°8 CALCUL INTEGRAL 2
- Lien entre aire sous la courbe
- COURS PRIMITIVES
- Cours INTEGRATION Partie I
- Cours INTEGRATION: Partie II
- Algorithme d'encadrement d'une
- FEUILLE 1 D'EX. INTEGRATION
- INFO FEUILLE 1 D'EX : INTEGRAT
- FEUILLE n° 2 D'EXERCICES
- INFO FEUILLE n°2 D'EXERCICES:
- FEUILLE n° 3 D'EXERCICES
- INFO FEUILLE n ° 3 D' EXERCICE
- INFO LISTE 1 D'EX. PRIMITIVES
- INFO 1 DEVOIR MAISON: 11 mai 2
- DS n°9 15mai 2007 TS1
- INFO DS n°9 15 mai 2007 TS1
- LISTE 1 D ' EXERCICE : PRIMITI
- INFO DV n°9 TS1 15 mars 20
- EX 1 BAC BLANC TS 20 mars 201
- EX 2 BAC BLANC TS 20 mars 201
- EX 3 BAC BLANC TS 20 mars 201
- EX 4 BAC BLANC TS 20 mars 201
- Tableau d'honneur bac blanc du
- NOTES BAC BLANC TS 20 mars 201
- INFO DV n°10 TS1 11 avril
- INFO EX 7 DV n°10 TS1 du 11 a
- INFO EX1 DV n° 9 TS samedi
- INFO EX 2 DV n° 9 TS 7 mars
TS Leçon n° 9 GEOM. DANS L' ESPACE
- Cours: Positions relatives dan
- Othogonalité dans l'espace
- Rappels sur le produit scalair
- INFO1 EX DEVOIR MAISON juin
- EX figure avec géoplan
- INFO 2 DEVOIR MAISON: juin 201
- INFO 3 DEVOIR MAISON JUIN 2012
- EXERCICE DE BAC GEOM ESP
- INFO EX BAC GEOM ESP
- INFO DV n°10 18 mai 2013 TS
- Entraînement7 mai 2014 TS1
- INFO Entraînement 7mai 2014 T
- INFO EX1 DV n° 10 TS1 21 m
- INFO EX2 DV n° 10 TS1 21 mar
- INFO EX3 DV n° 10 TS1 21 mar
- DV n° 10 TS1 21 mars 2015
- INFO EX1 BAC BLANC 25 mars 201
- INFO EX 2 BAC BLANC 25 mars 20
- INFO EX3 BAC BLANC 25 mars 201
- INFO EX4 BAC BLANC 25 mars 201
- Image pour ex de bac
- DS TS1 du 18 / 4/ 15
- INFO EX 1 DS TS1 18 avril 2015
- INFO Ex 2 DS 18 avril 2015
- INFO EX 3 DS 18 avril 2015
- Travail à faire avril 2015 TS1
- INFO Travail à faire avril 201
- TABLEAU D'HONNEUR DS TS1 du 18
TS REVISIONS
- INFO EX 1 BAC JUIN 2012
- INFO EX 2 BAC JUIN 2012
- INFO EX 3 PARTIE A BAC J
- INFO EX 3 PARTIE B BAC J
- INFO EX 3 PARTIE C BAC J
- INFO DEBUT EX 4 BAC JUIN 20
- INFO FIN EX 4 BAC JUIN 2012
- EX BAC PROBA
- INFO EX PROBA BAC
- EXERCICE BAC CALCUL INTEGRAL
- INFO EX BAC CALCUL INTEGRAL
- ROC SUR LES SUITES
- EX 1 NOMBRES COMPLEXES
- EX2 NOMBRE COMPLEXES TS
- INFO EX2 BAC JUIN 2011
- INFO EXERCICE :Loi Binom. Loi
- EXERCICE: Loi Binom. et Expon
- INFO QCM :COMPLEXES TS
- QCM: COMPLEXES TS
- EXERCICE : Géométrie dans l'es
- ROC SUR LES SUITES
- EXERCICE SUR LES SUITES
- INFO EXERCICE SUR LES SUITES
- EXERCICE: Lois exponentielles
- INFO EXERCICE sur Les lois exp
SUJET DE BAC S juin 2019
- SUJET BAC mars 2023 Métropole
- SUJET BAC S Juin 2019
- EX1 Oblig. Juin 2019 INFO
- EX2 Oblig. Juin 2019 INFO
- EX3 Oblig. Juin 2019 INFO
- EX4 Oblig. Juin 2019 INFO
- EX4 spé math Juin 2019 INFO
- Commentaires sur bac S 2019
- Sujet EXERCICE 1 BAC 2018
- Sujet EXERCICE 2 BAC 2018
- Sujet EXERCICE 3 BAC 2018
- Sujet EXERCICE 4 Oblig. 2018
- Sujet EXERCICE 4 SPE 2018
- Corrigé bac S 2018 EXERCICE 1
- Corrigé bac S 2018 EXERCICE 2
- Corrigé bac S 2018 EXERCICE 3
- Corrigé EXERCICE 4 SPE 2018
- Corrigé bac S 2018 EXERCICE 4
- Commentaires sur le bac 2018
- EX 1 bac S 21 juin 2017
- EX 2 bac S 21 juin 2017
- EX 3 bac S 21 juin 2017
- EX 4 oblig bac S 21 juin 2017
- EX 4 bac S SPE 2017
- INFO EX 1 bac S 21 juin 2017
- INFO EX 2 bac S 21 juin 2017
- INFO EX 3 bac S 21 juin 2017
- INFO oblig EX 4 S 2017
- INFO EX 4 SPE Métropole 2017
- INFO EX 1 S 2016
- INFO EX 2 S 2016
- INFO EX 3 S Spé 2016
- INFO EX 4 S 2016
- TEST 26 janvier 2016
- Conseils.
- ESPRIT DE L'ORAL BAC S
- Exemple 1 de sujet d'oral S
- Exemple 2 de sujet d'oral S
- Exemple 3 de sujet d'oral S
- Exemple 4 de sujet d'oral S
- Exemple 5 de sujet d'oral S
- Exemple 6 de sujet d'oral S
- EXERCICE 1 sujet 2015
- EXERCICE 2 sujet 2015
- EXERCICE 3 sujet 2015
- EXERCICE 4 sujet 2015
- TABLEAU D'HONNEUR TS1 juin
- EXERCICE 1 BAC S 2014 S
- EXERCICE 2 BAC S 2014 S
- EXERCICE 3 BAC S 2014 S
- EXERCICE 4 BAC S 2014 S
- http://www.mathemaths.com/page
- Bac 2023
TS1 AP TS1
- AP 14/09/2013 TS1
- REVISIONS : bases algébriques
- INFO REVISIONS: bases alg.
- AP 21/09/2013 TS1
- AP 28/09/2013 TS1
- AP 05/10/2013 TS1
- FEUILLE D' EXERCICES REVISIO
- INFO FEUILLE D' EXERCICES REVI
- AP 12/10/2013 TS1
- AP 19/10/2013 TS1
- QUESTIONS SUR LES NOMBRES COM
- INFO QUESTIONS SUR LES NOMBRE
- AP 09/11/2013 TS1
- AP 16/11/2013 TS1
- AP 5 avril 2014 TS1
- AP du 2 oct. et 13 nov. 2014
- AP du 11 déc. 2014
- AP du jeudi 8 janvier 2015
- AP du jeudi 5 février 2015
- AP du jeudi 19 mars 2015
- AP du jeudi 16 avril 2015
- AP du jeudi 28 mai 2015
TS...........Leçon 1 SUITES
- 2.COURS Résumé : suite TS sept
- Leçon n°1 TS SEPT 2012
- Leçon n° 1 TS INFO ACTIVITE
- 3.COURS Résumé Suites TS sept
- 4.COURS Résumé SUITES TS
- Feuille 1d'ex suites
- 5. COURS SUITES TS SEPT 201
- INFO EX 1 Feuille d'ex sur les
- 6. COURS SUITES TS Sept 20
- INFO EX 2 Feuille d'ex sur les
- DV n°1 TS pour le 21/09/12
- INFO EX 3 Feuille d'ex sur les
- INFO EX 4 Feuille d'ex sur les
- INFO DV n° 1 SUITES TS Sept
- INFO EX 5 Feuille d'ex sur les
- AIDE pour le DV n°1 TS1 du 21/
- FEUILLE 2 d'ex suites TS
- EXERCICE 6
- INFO EX 1 Feuille 2 suites TS
- 1.COURS SUITES TS sept 2012
- INFO EX 2 Feuille 2 suites T
- INFO EX 3 Feuille 2 suites TS
- INFO EX 4 Feuille 2 suites T
- INFO EX 5 Feuille 2 suites TS
- LES R.O.C 1 sur les suites
- LES R.O.C 2 sur les suites
- LES R.O.C 3 sur les suites
- ROC 4 SUITES
- TEST 1 SUITES TS S
- INFO TEST n° 1 SUITES TS S
- BAC 2008 LIBAN Série S
- INFO 1 EX BAC 2008 LIBAN Série
- INFO 2 EX BAC 2008 LIBAN Série
- FEUILLE 3 d'ex suites TS
- INFO EX 1 FEUILLE 3 d'ex sur l
- INFO EX 2 FEUILLE 3 d'ex sur
- INFO EX 3 FEUILLE 3 d'exercice
- DV n° 2 TS pour le 05/10/12
- AIDE pour le DV n° 2 TS1 du 05
- EXERCICE : Suite géométrique
- EXERCICE : Suite récurrente TS
- EX 1:Sur les formes indétermin
- EX 2: Sur les formes indétermi
- EX 3: Sur les formes indétermi
- EXERCICES:WEB d'une suite TS S
- DS n°1 TS 29/09/12
- INFO EX 1 DS n° 1 TS 29 / 09 /
- INFO EX 2 DS 1 TS1 29 / 09/ 12
- AP2 du MATHS 29/ 09 /12
- INFO AP 2 du vendredi 28 sept
- EX en demi groupe 28/09/12
- INFO EX en demi groupe 28 / 09
- INFO EXERCICE 1 DV 2 TS 5/10/
- INFO EX 2 DV 2 TS1 5/10/12
- INFO EX 3 DV 2 TS 05/ 10/12
- Devoir n°1 TS1 16 septembre 20
- INFO DV n°1 TS1 16 sept 2014
- DV n° 2 TS1 27 sept 2014
- INFO DV n°2 TS1 27 sept 2014
- TEST de Cours : SUITES TS
- INFO TEST de Cours : SUITES
- Dv n° 3 TS1 maison 11 octobre
- INFO Dv n° 3 TS1 maison 11 oc
- INFO EX de bac 2014
- EX BAC 2014
- DS n° 1 TS1 4/10/14
- INFO DS n° 1 TS1 4/10/14
- Tableau d'honneur DS n° 1 TS1
TS SUITES
- DS n° 6 TS2 13 fév 2012
- INFO EX 2 FIN DS n° 6 TS2 13/02/12
- TEST SUITES
- INFO TEST SUR LES SUITES
- TEST2 SUITES
- INFO TEST2 SUITE
- Explications ludiques sur le raisonnement par récurrence
- INFO EXERCICE SUITE ET ARITHMETIQUE
- EXERCICE SUITE ET ARITHMETIQUE
- SUITE DE SOMMES PARTIELLES
- EXEMPLE D'ÉTUDE DES VARIATIONS D'UNE SUITE
- INFO ÉTUDE DU SENS DE VARIATION D'UNE SUITE
TS .......................Leçon n°6 TS Fonction ln et primitives
- Résumé sur la fonction ln
- COURS: Fonction ln
- COURS: PRIMITIVES
- FEUILLE n° 1 D'EXERCICES Ja
- FEUILLE n°2 D'EXERCICES janv
- INFO TEST EX Ln Exp TS1 26
- TEST sur ln et Exp TS1 Sam
- FEUILLE D'EX n°2 Primitives
- DS n° 6 TS1 9 février 2013
- INFO EX 1 DS n° 6 TS1 9 févrie
- INFO EX 2 Partie A DS n° 6 T
- INFO EXE 2 Partie B DS n° 6 T
- INFO EX 2 Partie C DS n° 6 sa
- INFO DEBUT EX 2 DV n°8 du 5
- INFO DV n°9 TS1 MARS 2013
- DS n° 5 TS1 samedi 10 janvier
- INFO Ds n°5 TS1 10 janvier 201
- TABLEAU D'HONNEUR DS n° 5 TS1
- INFO DV n° 7 TS 17 janvier 2
- DV n°7 TS 17 janvier 2015
Leçon.................n°7 Probabilité conditionnelle
- Cours : Proba.conditionnelles
- INFO LISTE D'EXERCICES 1
- LISTE D'EXERCICES 1
- INFO DV n° 8 TS 31 janvier 20
- DV n°8 TS 31 janvier 2015
- INFO EX1 BAC BLANC 12 février
- INFO EX 2 BAC BLANC 12 fév 201
- INFO EX3 BAC BLANC 12 fev 2015
- INFO EX 4 BAC BLANC fév 2015
- SUJET BAC BLANC 12 fév 2015
- Bac Blanc fév 2015 Tableau d'h
TS...........Leçon 2 COMPLEXES
- FEUILLE 1 d'ex sur les nombres
- INFO FEUILLE 1 sur les nombres
- DV n° 3 TS1 pour le 19/10/12
- AIDE 1 DV n °3 TS 19/10/12
- AIDE 2 DV n °3 TS 19/10/12
- EX BAC INDE AVRIL 2006
- INFO EX BAC S 2006 INDE
- FEUILLE n° 2. EX Nombres Compl
- INFO FEUILLE n ° 2 COMPLEXE
- INFO DV n° 3 TS 19 / 10/12
- FORMULAIRE TRIGO
- DV n° 4 TS pour le mardi 13 no
- DS n° 2 TS Samedi 27 octobre
- INFO DS n° 2 TS 27 oct. 2012
- INFO DV n°4 TS1 13nov 2012
- Activités sur les complexes
- DS n°2 8 /11/13 TS1
- INFO DS n°2 8 / 11/ 2013
- DV n° 4 TS1 20 novembre 2013
- TABLEAU D'HONNEUR DS n° 2 TS1
- INFO DV n° 4 TS1 mercredi 20 n
- Dv n° 4 TS1 maison 8 nov 2014
- INFO DV n°4 TS1 08 nov. 2014
- INFO DS n° 2 TS1 18/10/14
- DS n° 2 TS1 18/10/14
- AIDE DV n° 4 du 8 nov 2014 TS1
- Tableau d'honneur DS n° 2 TS1
- U inclus dans C
- Feuille 2 de U inclus dans C
- Activité sur U inclus dans C
- INFO ACTIVITE
- ACTIVITE 1
- INFO ACTIVITE 1
- EXEMPLE D'ACTIVITE MATHS EXP
- INFO ACTIVITE SUITE COMPLEXE
- INFO 2 ACTIVITE SUITE COMPLEXE
- LOGIQUE POUR RACINE DEUXIEME
- RACINE 2 ième de 1 + i DANS C
- THÈME : Résolution de Z ² + 2
- ENSEMBLE DE MANDELBROT
TS............Leçon n° 3 LIMITES CONTINUITE
- Leçon n° 3 Limites et continui
- DV n° 5 TS1 27 nov 2012
- EX bac . Th de la bijection
- EX sur le Th de la bijection
- DICHOTOMIE : PRGM TI 84
- Th valeurs intermédiaires
- Rappel et complément : Limites
- EX 2 DICHOTOMIE
- LISTE 1 D'EX LIMITE-CONTINUITE
- INFO LISTE1 EX LIM-CONT
- INFOTP 1 TS1 nov 2012 LI
- TP 1 TS1 novembre 2012
- LISTE1 d'exercices TS1 LIMIT
- DS n°3 TS1 Samedi 24 novembr
- INFO DS n° 3 TS1 Samedi 24
- INFO EX1 DV n°5 TS1 mardi 27
- INFO EX4 DV n°5 TS1 mardi 27
- INFO EX 3 DV n° 5 TS 1 27
- INFO EX2 DV n°5 TS1 27 novemb
- BULLETIN TRIM 1 déc 2012
- INFO TEST : Limite, Continuité
- Test: Limite Continuité Th de
- DS n° 3 TS1 vendredi 22 nov.
- INFO DS n° 3 TS1 vendredi 22
- TABLEAU D'HONNEUR DS n° 3 TS
- TS1 Moyenne provisoire au 26 n
- DICHO Avec la Casio
- INFO 3 FEUILLE 1 SUR LES NOMBR
TS ...................Leçon.n°5 TS Fonction Exp
- Résumé sur la fonction exp
- FEUILLE D'EX sur les prop de l
- INFO FEUILLE D'EX sur les pro
- FEUILLE D'EX n°2 fonction ex
- INFO FEUILLE D'EX n°2 Fonction
- FEUILLE n° 1 EX FONCTION EXP
- INFO EX1 FEUILLE 1 FONCTION
- INFO EX2 FEUILLE 1 Fonction
- INFO EX3 FEUILLE 1 Fonction E
- INFO EX4 FEUILLE 1 FONCT
- INFO EX5 FEUILLE 1 FONCTION E
- INFO EX 6 FEUILLE 1 FONC
- TS1 DS n°4 TS1 22 décembre 2
- INFO EX1 DS n° 4 TS1 22 décemb
- INFO EX 2 DS n °4 TS1 2012
- INFO EX3 DS n° 4 TS1 22 décemb
- DV n° 7 TS1 12 janvier 201
- EX1 DV n° 7 TS1
- INFO EX 1 DV n°7 TS1 12 /
- EX 2 DV n° 7 TS1 12 /01/13
- INFO EX2 DV n° 7 TS1 12/01/13
- INFO EX3 DV n°7 TS1 12 /01/1
- EXERCICE 3 DV n°7 TS1 12/01
- INFO EX 4 DV n° 7 TS1 12 / 0
- EX 4 DV n° 7 TS1 12/01/13
- INFO EX 5 DV n° 7 TS1 12
- EXERCICE 5 DV n° 7 TS1 12
- INFO EX 6 DV n°7 TS1 12
- EX 6 DV n° 7 TS1 12 / 01
- DV n° 6 TS1 pour le 8 janvie
- FEUILLE D'EXERCICE n°2 Leçon
- INFO DS n° 4 21 /12/13 TS1
- DS n° 4 21/12/13 TS1
- TABLEAU D'HONNEUR DS n° 4 TS1
- INFO DV n° 6 TS1 8/01/14
- DV n° 7 TS1 pour le 22 janvi
- TEST 15 janvier2014 TS1
- INFO TEST 15 janv.2014 TS1
- TABLEAU D'HONNEUR DS n° 5 TS
- INFO EX 1 DV n°7 TS1 22 ja
- INFO EX 2 DV n° 7 22/1/14
- INFO EX3 DV n° 7 22/1/14 TS1
- AIDE DV n° 7 du 22 / 1/ 14
- Plan Salle 112
- INFO EX 1 Dv n° 6 TS1 13 déc
- INFO EX 2 DV n° 6 du 13 déc.
- INFO EX 3 et 4 DV n° 6 du 13
- PARTIE B d'un ex de bac S juin
- DS n° 4 TS1 13/12/14
- INFO DS n° 4 13/12/14 TS1
- TABLEAU D'HONNEUR DS n° 4 TS1
TS............Leçon n° 4 COMPLEMENT DERIVATION
- COURS: DERIVATION DE LA COMPOS
- DV n° 6 TS1 18 décembre 201
- INFO EX1 DV n°6 TS1 mardi 18
- INFO EX 3 DV n°6 TS1 mardi 1
- INFO EX 2 DV n°6 TS1 M
- INFO FEUILLE D'EXERCICE n°1 L
- FEUILLE D'EXERCICE n°1
- EXERCICES
- Moyenne TRIM 1 TS1 déc. 2013
- INFO DV n°5 TS1 6 déc. 201
- Feuille d'ex Leçons 3 et 4 TS
- INFO DS n° 3 15/11/14 TS1
- DS n° 3 15 / 11 / 14 TS1
- Dv n° 5 TS1 maison 22 nov 201
- Tableau d'honneur DS n° 3 TS1
- INFO Dv n° 5 TS1 maison 22 o
- BULLETIN TRIM 1 Nov 2014
- INFO FEUILLE D'EXERCICES
- FEUILLE D'EXERCICES TS1 13
- INFO EX SUR LA METHODE D'EU
- EX SUR LA METHODE D'EULER
- Exercice sur les sinus et cosi
TES Spécialité math.
- INFO TEST 1 SPE MATH TES
- INFO EX BAC SPE 29 MARS 2012
- EX BAC BLANC TES SPE 29 MARS2012
- DV Maison TES EX 2 Partie 3 Lundi 6 février 2012
- DV Maison TES EX 2 PARTIE 1 Lundi 6 février 2012
- DV Maison TES INFO SECONDE PARTIE DE EX 2 Lundi 6 février 2012
- TEST TES DU 30 JANVIER 2012
- INFO EX BAC ES ANTILLES-GUYANE
- EX BAC ES ANTILLES-GUYANE2007 SUITES
- EXERCICE SPE MATH
- INFO EXERCICE BAC ES spé
- INFO DS n° 4 TES 12/12/11
- DS n° 4 TES 12 décembre 2011
- INFO 1 DV n° 2 Maison TES Spé
- TD 1sur les surfaces TES Spé
- DS n° 3 Spé TES 14/11/11
- TEST GEOMETRIE DANS L'ESPACE
- INFO 2 DV n° 2 Maison TES spé
- EXERCICE matrices et graphe TES spé
- INFO EX 4 BAC ES SPE 2013
TES 2012 ; 2013 ; 2014 spécialité
- ACTIVITE MATRICES TES SPE MATH
- Problème TES OCT 2013
- EX : Leçon Matrices
- DSn°1 TES SPE 08 / 10 /12
- INFO Problème TES OCT 2013
- DS n°1 TES spé 14 / 10/2013
- INFO DS n° 1 TES SPE 14 oct 2
- TABLEAU D'HONNEUR DS n° 1 TES
- MODELISER EX 1
- INFO TEST n° 2 TES SPE 18 nov
- TEST n° 2 TES SPE du 18 novem
- Notes
- MOORE TES Déc.2013
- INFO DS n° 1 8 /10/12 TES s
- INFO Problème1 bac ES spé
- Problèmes bac ES spé
- INFO Problèmes 2 bac ES spé
- INFOTEST TES Spé décembre 2011
- TEST TES spé décembre 2011
- INFO DS n° 2 TES SPE 18 no
- TES DS n°2 spé maths 18 nov
- TEST TES Spé 10 décembre 2012
- INFO EX 1 TEST TES 10 décembr
- INFO EX2 TEST TES Spé 10 Déc 2
- NOTES DU DS n° 3 du 16 / 12 /
- Moore-DijKstra Pondichéry
- TABLEAU Moore-Dijkstra Asie
- TABLEAU Moore-Dijkstra Polynés
- EXERCICE SURE LES GRAPHES
- EXERCICE 4 SUR LES GRAPHES
- INFO DS n°4 TES spé maths 27
- NOTES DU DS n° 4 du 27 / 011 /
- TES DS n°4 spé maths 27 janv
- INFO EXERCICE de bac du TEST
- NOTES TRIM 2 TES SPE
- Bac Blanc EX SPE TES 21 mars
- Notes EX spé. math. Bac blanc
- EX DE BAC Tableau de Moore
- France Métropolitaine TES 2
- EX Bac ES Pondichéry 2013
- Travail à faire pour s'entraîn
- Test des bases de cours:
- Test des bases de cours
- INFO EX BAC LIBAN 2014 ES spé
- EX BAC LIBAN 2014 spé maths
- INFO Feuille d'ex TES sur les
- DS n° 1 TES spé 13/10/14
- INFO DS n ° 1 TES spé 13 /10 2
- DV maison 10 nov 2014 TES Spé
- INFO TEST TES SPE 01/12/14
- TEST TES SPE 01/12/14
- INFO EX spé bac 2009
- EX DE BAC ES SPE 2009
- INFO TEST 9 décembre 2013
- TEST du 9 déc 2013
- EX BAC SPE 2014 ES Métropole
- SUJET SPE 2014
- INFO TEST SPE MATH. 26 janvi
- TEST TES SPE 26/1/15
- INFO BAC BLANC 13 février 201
- Tableau d'honneur bac blanc T
- Ex bac ES Pondichéry avril 2
- Texte complet de l'exercice du
- EX1 bac ES 2015
- EX2 bac ES 2015
- EX4 bac ES 2015
TS....... Leçon sur les PROBABILITES
- INFO TEST EX de bac donné le
- NOTES DU TEST TS 08/02/14
- V.a.r indépendantes
- TS1 INFO EX1 BAC BLANC 15 fév2
- TS1 INFO EX2 2 BAC BLANC 15 fé
- TS INFO EX 3 BAC BLANC TS 15/2
- TS INFO EX4 BAC BLANC TS 15/2/
- FIN DE L'EXERCICE DE RÉVISION
- Tableau d'honneur bac blanc du
- INFO DV n°8 TS1 5 mars 201
- AIDE 1 DV n ° 8 à la maison TS
- AIDE 2 DV n ° 8 à la maison
- AIDE 3 DV n ° 8 à la maison T
- MOYENNE TRIM 2 TS1
INFO EX 77 DV maison TS2 05 /12/11
. INFO DV MAISON TS2 5/12/11
EXERCICE 77 page 61
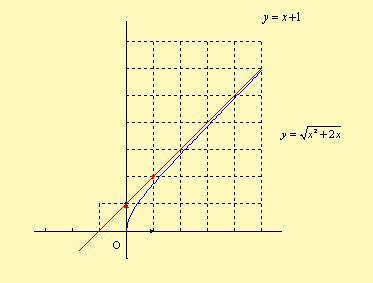
Soit la fonction f : x → √( x2 + 2 x )
a. Etudier le sens de variation de f sur l'intervalle [ 0 , + ∞ [.
b. Déterminer limf ( x )
x → + ∞
c. Démontrer que la droite d'équation y = x + 1 est une asymptote
à la courbe de Cf en + ∞.
d . Tracer Cf et son asymptote dans un repère orthonormal.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Réponse:
a. Sens de variation de f .
Soit la fonction polynôme u : x → x2 + 2 x
u est définie et dérivable sur IR.
u > 0 sur l'intervalle ] 0 , + ∞ [.
Donc la fonction √u , c'est-à-dire f , est définie et dérivable sur
l'intervalle ] 0 , + ∞ [.
Ainsi : f ' = ( √u )' = u ' / ( 2 √u )
On a : u ' : x → 2 x + 2
Donc f ' : x → ( 2x + 2 ) / ( 2 √ ( x2 + 2 x ) )
c-à-d f ' : x → ( x + 1 ) / √ ( x2 + 2 x )
Comme x + 1 > 0 et √ ( x2 + 2 x ) > 0 quand x > 0
on a : f ' > 0 sur l'intervalle ] 0 , + ∞ [.
Conclusion : f est strictement croissante sur ] 0 , + ∞ [.
b. Limite de f en + ∞.
On a : lim ( x2 + 2 x ) = + ∞.
x → + ∞
et
lim √X = + ∞
X → + ∞
D'où comme limite de la composée de deux fonctions
lim √( x2 + 2 x ) = + ∞
x → + ∞
Conclusion : lim f( x ) = + ∞
x → + ∞
c. Asymptote D : y = x + 1 en + ∞
Soit x > 0
On a : f( x )- ( x + 1 ) = √( x2 + 2 x ) - ( x + 1 )
c-à-d en multipliant et en divisant par l'expression conjuguée
f( x )- ( x + 1 ) = [ √( x2 + 2 x ) - ( x + 1 ) ] [ √( x2 + 2 x ) +( x + 1 )] / [ √( x2 + 2 x ) +( x + 1 )]
c-à-d
f( x )- ( x + 1 ) = [ ( √( x2 + 2 x ))2 - ( x + 1 )2 ] / [ √( x2 + 2 x ) + ( x + 1 ) ]
c-à-d
f( x )- ( x + 1 ) = [ x2 + 2 x - ( x2 + 1+ 2 x ) ] / [ √( x2 + 2 x ) + ( x + 1 ) ]
c-à-d
f( x )- ( x + 1 ) = - 1 / [ √( x2 + 2 x ) + ( x + 1 ) ]
Or √( x2 + 2 x ) + ( x + 1 ) > x + 1 sachant x > 0
et lim ( x + 1 ) = + ∞
x → + ∞
D'où lim ( √( x2 + 2 x ) + ( x + 1 ) ) = + ∞
x → + ∞
Ainsi lim - 1 / [ √( x2 + 2 x ) + ( x + 1 ) ] = - 1 / ( + ∞ ) = 0
x → + ∞
Donc lim ( f( x ) - ( x + 1 ) ) = 0
x → + ∞
Conclusion : La droite D : y =x + 1 est bien une asymptote oblique
en + ∞ à la courbe de f .
d. Courbe : Voir plus haut.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------